SMALL
문제
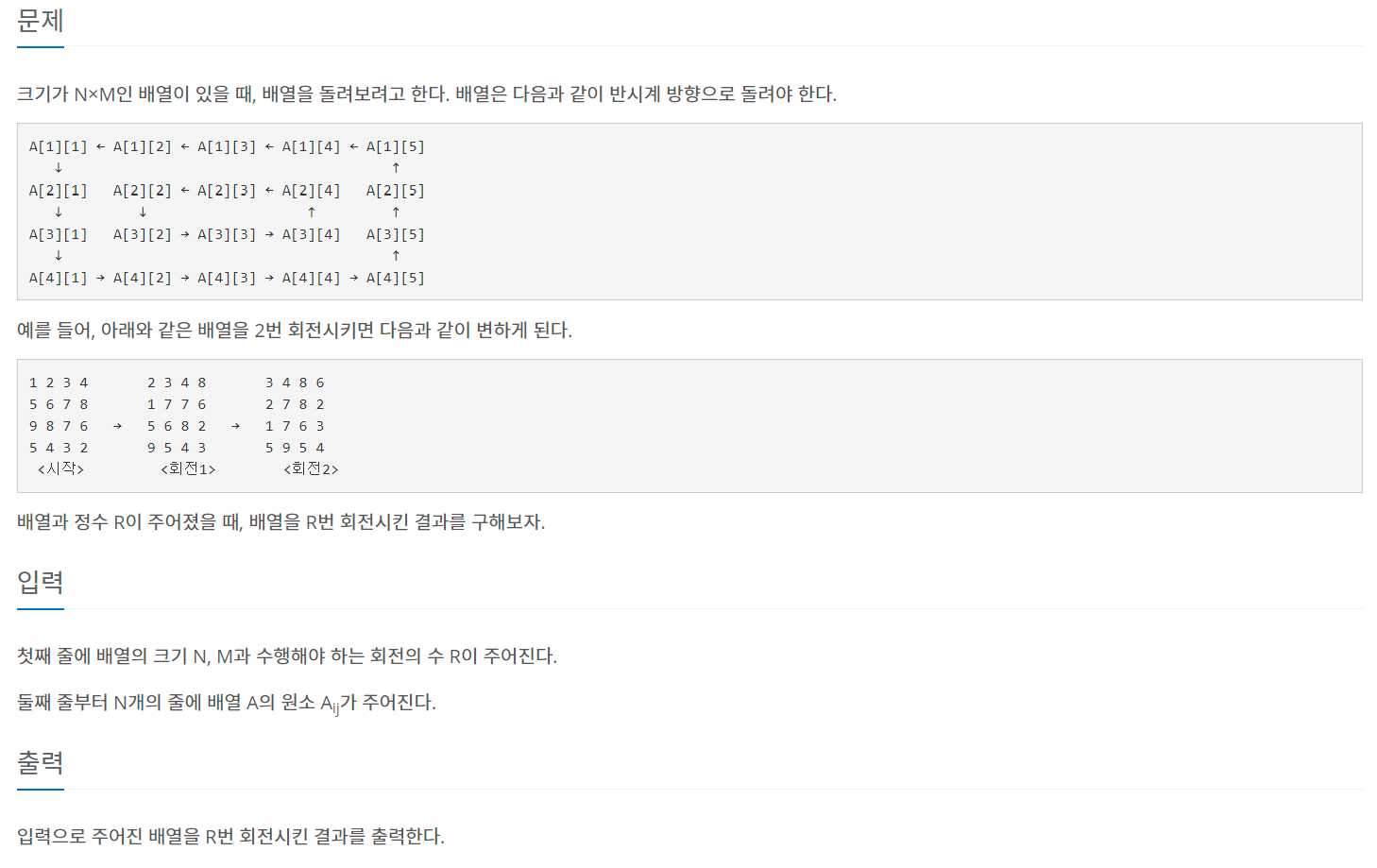
- 구현의 기본적인 문제
- 반시계방향으로 배열의 각 원소를 하나씩 옮긴다.
- R번 회전한다.
해설 및 코드
배열 회전 문제를 구현할 때, 그냥 보이는 대로 푸는 경우가 많다.
-> 복잡성이 증가한다. 내가 구현한 배열 회전은 2개의 temp를 임시저장해서 사용했다.
완전히 같은 문제는 아니지만, 배열 돌리는 문제를 부딪치면서 푼 방법이다.
int stx = queries[i][0];
int sty = queries[i][1];
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int endx = queries[i][2];
int endy = queries[i][3];
int back = map[stx][endy];
for (int j = endy; j > sty; j--) {
min = Math.min(min, map[stx][j]);
map[stx][j] = map[stx][j-1];
}
min = Math.min(min, back);
int back1 = map[endx][endy];
for (int j = endx; j > stx; j--) {
min = Math.min(min, map[j][endy]);
map[j][endy] = map[j-1][endy];
}
map[stx+1][endy] = back;
min = Math.min(min, back1);
back = map[endx][sty];
for (int j = sty; j < endy; j++) {
min = Math.min(min, map[endx][j]);
map[endx][j] = map[endx][j+1];
}
map[endx][endy-1] = back1;
min = Math.min(min, back);
back1 = map[stx][sty];
for (int j = stx; j < endx; j++) {
min = Math.min(min, map[j][sty]);
map[j][sty] = map[j+1][sty];
}
map[endx-1][sty] = back;
한 눈에 봐도 복잡해 보이는 방법
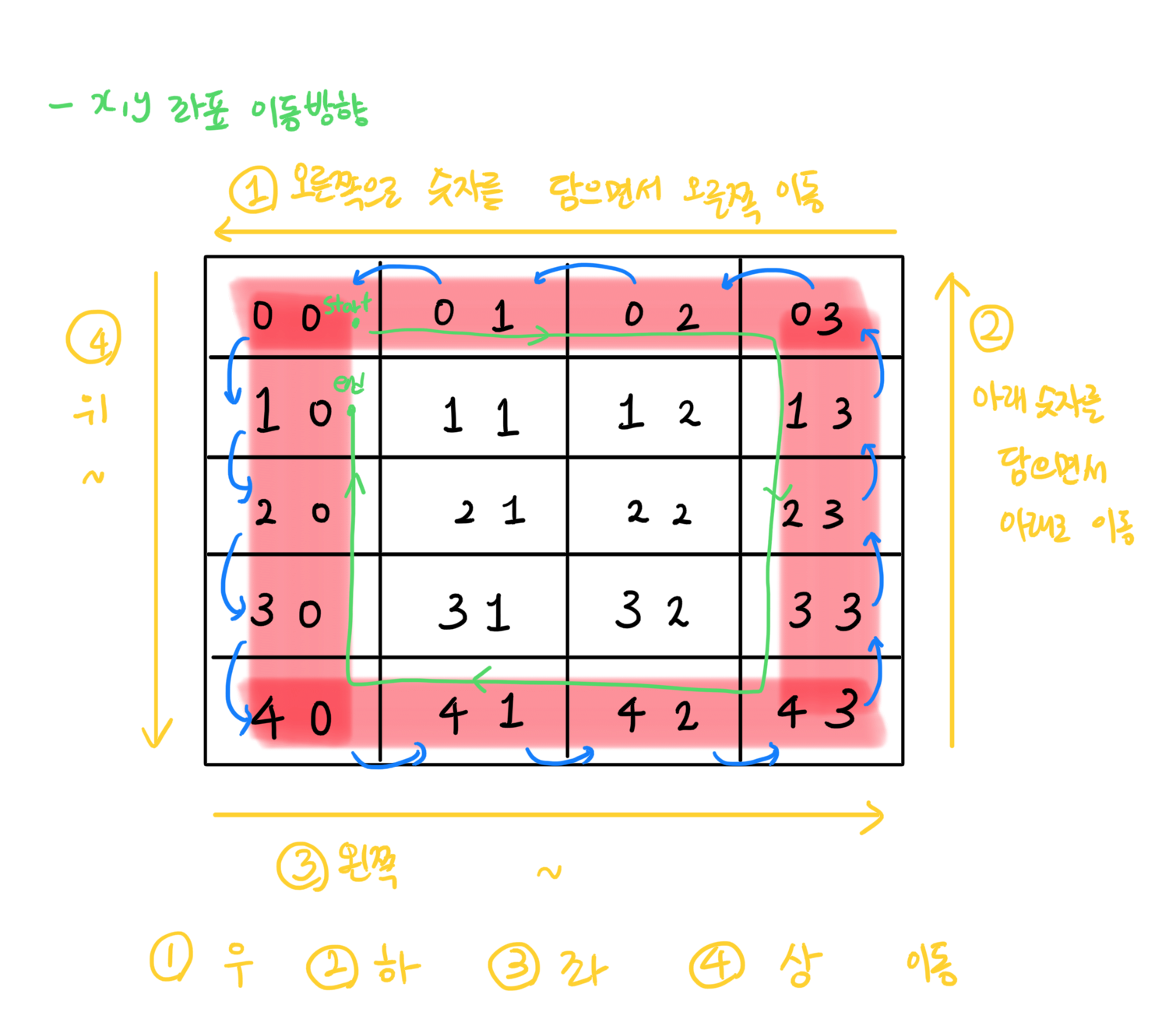
따라서, 사방탐색을 이용해 최대한 간단하게 구현했다.
package BAEKJOON;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class 배열돌리기1_16926 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt(); // 배열의 세로
int M = sc.nextInt(); // 배열의 가로
int R = sc.nextInt(); // 회전 횟수
int[][] map = new int[N][M];
// 배열 채우기
for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < map[0].length; j++) {
map[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
// 우 하 좌 상 --> 반시계방향
int[] dr = { 0, 1, 0, -1 };
int[] dc = { 1, 0, -1, 0 };
// R만큼 반복한다.
for (int r = 0; r < R; r++) {
// 가로, 세로 중 작은 것의 절반만큼 회전해야하는 사각형이 나온다.
for (int cnt = 0; cnt < Math.min(N, M) / 2; cnt++) {
// 첫 번째 숫자를 기억해야한다. save_point
int sp = map[cnt][cnt];
// 시작점
int x = cnt;
int y = cnt;
// dr, dc의 index
int i = 0;
// 4 방향을 다 돌면 종료한다.
while (i < 4) {
// 반시계방향으로 배열이 회전하므로, (x, y)에 들어가야 할 위치를 찾음
int cx = x + dr[i];
int cy = y + dc[i];
// 범위를 벗어나면 index를 증가시키고 덮어쓰기는 진행하지 않음
if (cx < cnt || cy < cnt || cx >= N - cnt || cy >= M - cnt) {
i++;
continue;
}
// 값 저장
map[x][y] = map[cx][cy];
// (x, y)는 이동한 좌표가 된다.
x = cx;
y = cy;
}
// 제일 마지막에 시작 값을 넣어준다.
map[cnt + 1][cnt] = sp;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
참고블로그: hidelookit.tistory.com/110
[백준 16296] 배열 돌리기 1 (자바)
백준 16296번 배열 돌리기 1 (자바) 출처 www.acmicpc.net/problem/16926 16926번: 배열 돌리기 1 크기가 N×M인 배열이 있을 때, 배열을 돌려보려고 한다. 배열은 다음과 같이 반시계 방향으로 돌려야 한다. A[1]
hidelookit.tistory.com
배열 돌리기는 코테에서 나올 때도 있다. 특히 삼성이 구현 + DFS/BFS를 좋아하므로 알아두면 좋다.
반응형
LIST
'IT > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [BOJ] 합이0 3151.java (0) | 2021.06.01 |
|---|---|
| [BOJ] 시리얼번호 1431.java (0) | 2021.05.18 |
| [알고리즘 이론] 카데인 알고리즘(Kadane's Alogrithm) (0) | 2021.03.23 |
| [BOJ] 소년점프 16469.java (0) | 2021.03.20 |
| [이코테BOJ] 플로이드 11404.java (0) | 2021.03.20 |



